Technical SEO for the success of your business
Technical SEO is the part of SEO that is responsible for your business fulfilling its potential online. When we talk about technical maintenance and improving site performance, it means achieving better ranking positions in search engines, benefiting your business.
Why is technical SEO important?
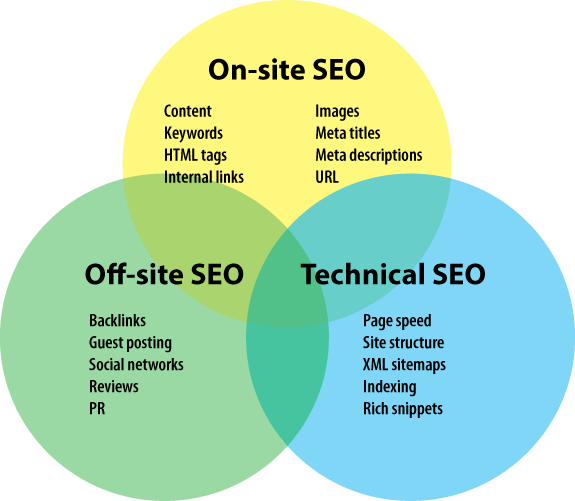
There are three types of SEO:
- On-Site SEO involves direct effort on the website or webpage which you’re trying to improve. For example, improving its content and adding additional keywords.
- Off-Page SEO involves efforts to add links to your site or other sites to help your page achieve a higher rank. For example, feedback, lists, social promotion, guest publishing, PR, etc.
- Technical SEO involves efforts related to the site’s exit code, site map, security, and structured data, which aren’t directly relevant to the content.
You can have the best website with the best content, but if it can’t be crawled properly, has technical errors, and loads slowly, it won’t rank at all. That’s why we offer our expertise in technical SEO, focusing on improving load speed, indexing, and overall optimisation of your website.
Google and other search engines need to find, crawl, render, and index the pages of your website.
For your site to be fully optimised technically, the pages must be secure, optimised for mobile devices, free from duplicated content, and load quickly, among thousands of other factors that are part of technical SEO.
This doesn’t mean that your technical SEO needs to be flawless. Some factors may be difficult to address without drastically changing your site.
However, the more accessible your website is for Google, the higher your chances are for ranking.
What is technical SEO?
Technical SEO – optimisation of loading speed or technical optimisation is the same thing. This is the process of optimising a website so it meets the technical requirements of contemporary search engines, aiming to improve organic ranking. Important elements of technical SEO include crawling, indexing, rendering, and website architecture.
Technical SEO aims to optimise sites so they can rank well in the online space and bring positive financial results to the business that has invested in this kind of maintenance. If you want a business that has incredible success, then technical SEO is the key to it. Let’s talk about your project starting from today!
How does indexing work?
Robots find pages, check the content in the pages, and use the links to the pages to find more. That’s how they find new pages. Here are some of the most important terms that you should know about indexing and its role in technical SEO:
- Crawling
Crawler is the system that search engines use to get content from pages.
- URL addresses
How do they start finding pages? They create a list of URL addresses that they have found through links. There are so-called maps of sites created by users of other systems that list all possible links for a website to make it easier for search engines to find all links.
- Crawling queue
When robots find pages that have to be crawled or crawled again, these pages are prioritised and added to the crawling queue.
- Processing systems
Processing systems manage with canonisation and send pages to the render and process them to find more URL addresses for crawling.
- Rendering
Renderer loads a page like a browser using JavaScript and CSS files to see it as users see it.
- Index
When Google indexes pages, they are ready to be shown to users. The index is saved pages which are crawled and rendered.
- Robots.txt
That’s the file that tells Google where it can and where it can’t go on your website. This is an important file because there may be pages that you don’t want or have to be indexed.
You may also want to have pages that are accessible for users only. Those are often inner networks, content only for members, test pages, and so on.
During technical optimisation, each of those parameters is followed and optimised until you’re satisfied.
Our checklist for technical SEO
When we’re talking about technical SEO, it doesn’t only mean your site needs to be crawled and indexed, but it also has to load fast, be intuitive, and convenient for clients, while being free of errors that might lead to wrong or non-existent pages. Technical optimisation is the foundation and walls of your digital presence. Without it, your awesome products will be unavailable and undetectable.
To optimise your site technically, we have to check and keep in mind:
- Design and architecture of the website
- Loading Speed
- Security
- XML map of the site
- Canonical URL addresses
- Hreflang tag
- Internal connection
- References and errors
- Content duplication
- Marking structured data
- Checking for missing meta titles and descriptions
- Noindex labels
All of these checks signal potential problems and guide us in applying our technical SEO skills.
Technical SEO – step by step
Before we start technical optimisation, we must check if you have accounts in the following tools on your site:
- Google Search Console (GSC)
- Google Analytics (GA)
- Bing Webmaster Tools
- Semrush
- Screaming Frog
- Ahrefs
Using these tools, we conduct the necessary checks and track changes. They are essential for technical SEO and help save time.
Google Search Console offers a free tool that is very useful. Not only does it check keywords, but it also tracks the technical condition of the site. As SEO specialists, we use software like SEMrush and Ahrefs, which provide better convenience and accuracy. As a next step, we recommend installing an SEO plugin on the site. We suggest RankMath, SEOPress, or AISEO, as they assist with audits and technical optimisation.
Architecture optimisation of a website
- Structure of a website
The structure of a website is of great importance for indexing your pages, making it a key step in technical SEO. A poorly designed structure can lead to various crawling issues. Optimising the structure can assist in better management of other types of optimisations, such as handling the count of URL addresses, dealing with blocked pages, and more.
Architecture of a website
To create a flat structure for a website, all of its pages should be interlinked with a few links to one another. This approach makes crawling easier for Google, especially for large websites. The structure is crucial to achieve the desired crawling efficiency. Links and levels should be kept to a maximum of three vertically and as needed horizontally.
When organising the architecture, we follow simple rules. When it’s related to including additional materials, applications and articles which provide additional value for a specific keyword.
We start an audit and build a semantic core, creating logical organised strong structure we put all of your pages in categories to help search engines understand your website better and to improve your ranking. That’s how a technical SEO is done correctly.
One detailed aspect of technical SEO is in product categories where 24 products are listed by default. This automatically adds keyword accumulation.
Similarly, articles with applications for a certain product can be a subcategory of the product page.
- Breadcrumbs
Breadcrumbs direct users back to the beginning of the website and show the path they took to reach that page.
Breadcrumbs are not only meant for user navigation but also for search engines. For users, breadcrumbs make navigation easier, allowing them to go back without using the browser’s back button. They have structured markup language, which provides clear context to search engine bots.

- Adaptive design
The aspect ‘first for mobile devices’ involves designing the desktop site starting with the mobile version first and then adapting it to the desktop site (contrary to the traditional approach of starting with the desktop site and then adapting it to smaller screens). In general, it means building the website first for mobile devices, as the main goal of technical SEO is to improve the user experience on mobile devices.
Statistics from data on device usage show that mobile device usage is over 80%. This makes us prioritize how your website will look on mobile devices and then adapt its version to the desktop.
- Pagination
Using pagination shows search engines how separate URL addresses are related to one another, making it easier for bots to find and crawl those pages. Pagination is often used when you want to divide a sequence of content into sections or multiple webpages.
Adding pagination in technical SEO is straightforward. You just need to rework the HTML file and include the <head> on the first page, using “rel=next” as a link to the second page. On the second page, you add “rel=prev” to go back to the previous page and “rel=next” to go to the next page.
Alternatively, you can modify the theme’s code to include automated pagination. Most themes allow this customisation.
The factors mentioned above are closely related to the next step and the first point in technical SEO, which is focused on improving users’ experience and increasing clients.
Loading speed optimisation
People who use the internet don’t like pages that load too slowly or move during loading. They may leave your page without even waiting for it to load. Search engines also dislike slow loading, and it can have an impact on your ranking. While a fast page doesn’t automatically guarantee a higher ranking, loading speed still plays a key role.
Our goal is to check how a page is loading, analyse any problems, and correct them. Many tools are used for technical SEO to help identify issues with page speed.
The quality of images and the use of caching can affect the size of a page, and using third-party scripts can slow down loading times.
Key factors which are tracked and help with technical optimisation include:
- Checking the web hosting
- Checking if the server is near your zone of service
- Checking if CDN is used
- Checking if GZIP compression is used
- Checking if server caching is used.
- Minification of JS/CSS files
- Checking the image size and extensions
- Compressing and optimising images
- Checking postponed loading of images and iframes (embedding YouTube, etc)
- Checking if plugins or modules are updated
- Optimising the database
This is one of the most important steps and is often underestimated which leads to various problems.
With improved loading after technical SEO…
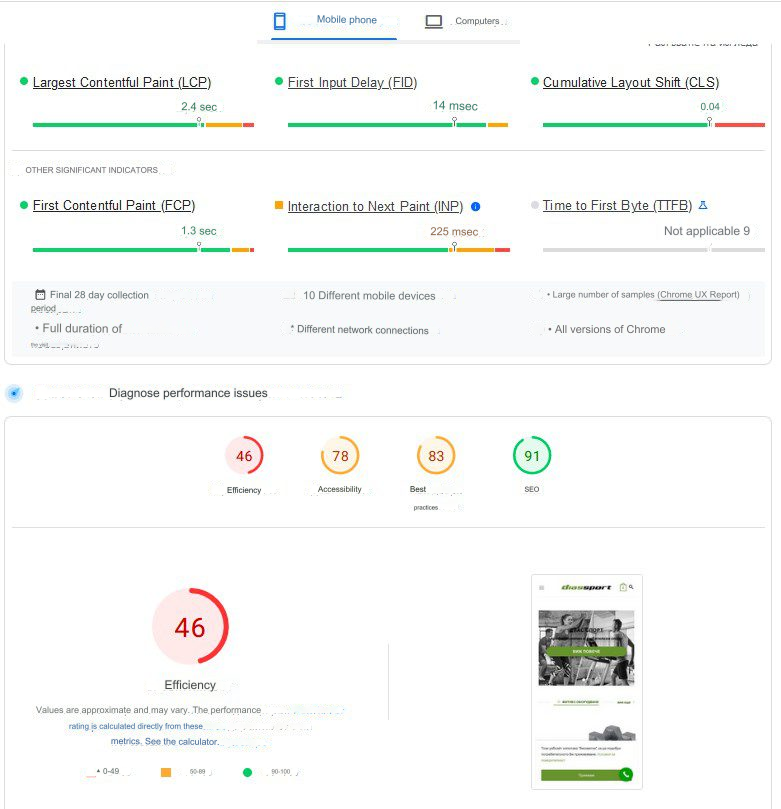
… we receive better crawling and indexing of the website.
This step is the most complex when it comes to realisation. If you don’t know any technical aspects, we recommend you to contact specialists.
Factors which we track and optimise in technical SEO are:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) – The time between the page loading and the loading of the largest content element on the page.
- Server Response Time
- Resource Size
- Third-Party Resources
- Large Images
- Unnecessary Plugins
- Blocking CSS/JavaScript, etc.
- First Input Delay (FID) – The time between the first user action on the page and the corresponding response from the page.
- Large Elements
- Third-Party Resources
- Blocking CSS/JavaScript
- Unnecessary Plugins, etc.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) – Measures unexpected layout shifts of visual elements on the page.
- Element Size Attributes
- Image Sizes
- Font Types, etc.
- JavaScript Execution Time
- CSS Execution Time
- First Contentful Paint (FCP) – The time between the page loading and the loading of the first content element on the page.
- Multiple Redirects
- Resources Blocking Content Display
- Unused CSS
- Number of Requests
- Caching Rules
- Server Response Time
- Large DOM Elements, etc.
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP) – Measures the time between user interactions like clicks or key presses and the subsequent rendering of the next page.
- Large Elements
- Third-Party Resources
- Blocking CSS/JavaScript
- Unnecessary Plugins, etc.
- Time to First Byte (TTFB) – The time between the request for a resource and the moment the first byte of the response starts arriving.
- Redirect Time
- Service Worker Startup Time (if applicable)
- DNS Lookup
- Connection and TLS Handshake
- Time until the first byte of the response arrives.
All these metrics in technical SEO are tracked and optimised. Reworking of files and the theme of the website is also required to achieve the desired results.
Security – SSL
Have you noticed the icon for locking the address line?
Well, this is a sign that the website is using the HTTPS protocol instead of HTTP. It is also called SSL – Secure Sockets Layer, which creates a protected encrypted connection between the browser and the server. In 2014, Google gave priority to HTTPS and announced that those sites would receive a better ranking. Now it’s 2023, and SSL isn’t just an advantage but a necessity and is mandatory.
When we create a website, that protocol is used by default. If you don’t have it, we can install an SSL certificate for you.
XML site map
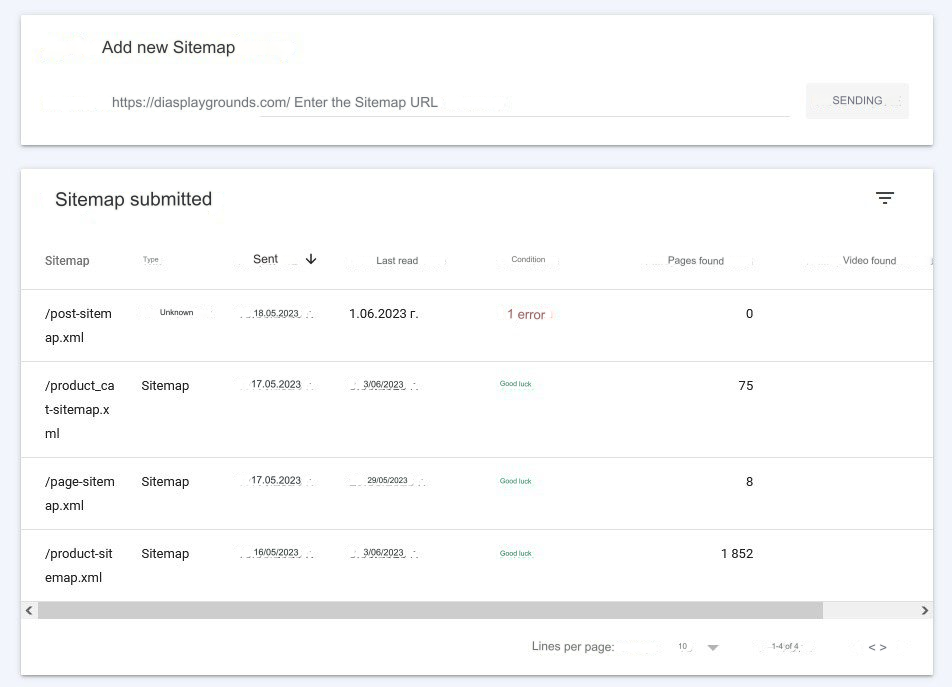
The sitemap is the file with the structure of your website. While Google can find pages by following links on your site, sitemaps are one of the most important sources for finding URL addresses. An XML sitemap not only lists your pages but also provides information such as when your pages were found, when they were changed, how often they are updated, and the priority of each page.
Even if you have a well-organised website, an XML sitemap won’t hurt. It’s very easy to create one if you don’t have it already. We recommend using separate sitemap files, as it makes it easier to track errors and ensure that everything is included.
Sitemap files can easily be set up and created using plugins like RankMath or AISEO.
Robots.txt
The first thing a bot does when crawling a website is to check the robots.txt file. It shows whether they can crawl specific pages or not, and what parts of pages they are allowed to crawl. This file is essential for controlling how bots interact with your website and what content they can access.
There are bad bots that may attempt to delete content or send spam in your forums. By properly configuring the robots.txt file, you can prevent these bots from crawling your pages and causing harm.
However, it’s important to be cautious when using robots.txt as it can unintentionally block CSS or JS files that are needed for search engines to properly evaluate your website. If these critical files are blocked, search engines won’t be able to open your pages and understand if your website is functioning correctly. During technical optimisation, the robots.txt file is checked to ensure that it is properly structured and optimised if necessary.
Here’s an example of the configuration of the robots.txt file when we apply technical SEO to websites created with WordPress.
“User-agent: *
Disallow: /wp-admin/
Allow: /wp-admin/admin-ajax.php
Sitemap: https://example.com/product_cat-sitemap.xml
Sitemap: https://example.com/product-sitemap.xml
Sitemap: https://example.com/page-sitemap.xml
Sitemap: https://example.com/post-sitemap.xml
Canonical URL Addresses
One of the ways to resolve the issue of duplicated content in technical SEO is by adding noindex tags.
Another effective method is to utilise canonical URL addresses. Canonical URL addresses are particularly beneficial for pages with highly detailed content, such as product pages that showcase the same product in different sizes or colours.
To address this matter, we include canonical tags in the <head> section of the duplicated pages, like this:
<link rel=”canonical” href=”https://example.com/sample-page” />
By adding the canonical tag, we specify the main page as the URL address for the duplicated pages. It’s important to ensure that noindex and canonical tags are not mixed, as this can lead to complications. If, for some reason, we need to use both tags, we implement a 301 redirection to handle it correctly. We make sure to use only one canonical tag per page, as Google ignores sets of canonical tags.
Hreflang
If your website supports multiple languages, it can result in duplicated content. To address this issue and help Google recognize that these are the same pages but in different languages, we use the hreflang attribute. This helps Google present the right version of the page to each user based on their language preferences.This technical SEO approach allows search engine bots to understand that these pages are variations of one another.
The hreflang looks like this:
<link rel=”alternate” hreflang=”lang_code” href=”url_of_page” />
We make sure to add this attribute to all the alternative language pages that we process. For more information about hreflang, you can refer to Google’s guidelines on the matter.
Optimising internal links
Internal links may not be considered a part of technical SEO, but they are worth mentioning. Having a flat website structure can be advantageous in this regard. In an ideal setup, the most distant pages should be only 3-4 links away from the main page and should also contain links to other relevant pages. As part of our technical SEO analysis, we check for any orphaned pages that have no internal links pointing to them.
Redirections and errors
During technical optimisation, we thoroughly check if the redirections are properly set up. Website maintenance is an ongoing process, and regular updates are necessary. Pages may be deleted or new ones created, and in such cases, it’s essential to set up proper redirections to relevant goods or services. Here is a list of common errors that we monitor in technical SEO and address every month:
- 301 Moved Permanently
- 302 Found (Previously “Moved temporarily”)
- 403 Forbidden
- 404 Not Found
- 405 Method Not Allowed
- 500 Internal Server Error
- 502 Bad Gateway
- 503 Service Unavailable
- 504 Gateway Timeout
To avoid errors, we regularly check URL addresses and ensure that we’re using the proper redirections. It’s important to remember that users and search engines dislike being directed to non-existent or incorrect pages.
Important note: Using too many redirections can slow down the loading speed of the page, and if more than three are used, search engines may refuse to crawl the page.
Checking and optimisation of duplicated content
When adding new products from your colleagues, there is often duplicated content, such as titles, meta descriptions, and meta titles. If automation is set up incorrectly, it can also lead to the same issue. While Google may tolerate some level of duplicated content for online stores, it considers it unacceptable for websites offering services.
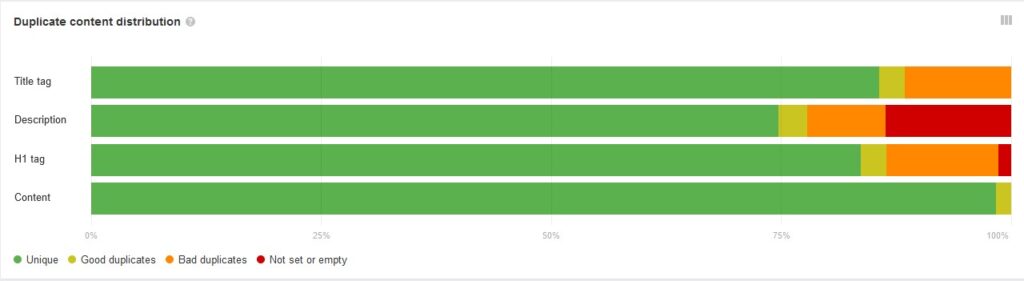
There are various methods to check if your website has duplicated content. We utilize Ahrefs and specifically examine the “Quality content” section to assess Duplicate content distribution.
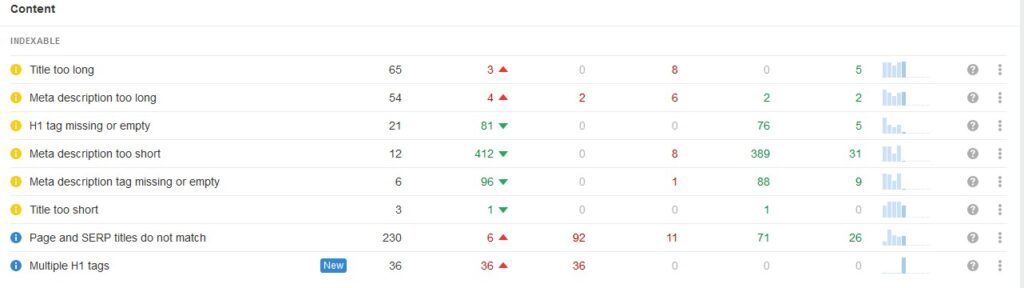
Checking for missing meta titles and meta descriptions
This check and optimisation are also part of on-site SEO, but they contribute to better rankings and attracting new clients. We mention it here because we use the modules mentioned above, such as RankMath, SEOPress, or AISEO, to quickly provide missing meta titles and descriptions by extracting information from the page or the product. However, we shouldn’t solely rely on them, as the results may not always be as desired.
Optimisation for enriched content
There isn’t definitive proof that schema or structured data markup directly influences search engine rankings. However, it can enhance the appearance of your website in search results and attract more clicks from users. By using structured data, you can add reviews, ratings, or product prices that may be displayed in SERPs.
Even if structured data doesn’t directly impact rankings, it can still have a positive effect on user engagement. Rich snippets provide valuable information to users, encouraging them to click on your page over others.
As part of technical SEO, various techniques are employed to improve the appearance of enriched results. Properly implemented schema markup can enhance the visual representation of your products and services, making it easier for clients to make informed decisions and potentially improving your overall ranking indirectly.
Noidex labels
You may have certain pages on your website that you don’t want to appear in search results, such as thank you pages or pages with duplicated content. In such cases, we use the “noindex” directive to instruct search engines not to index those pages.
The noindex looks like this:
<meta name=”robots” content=”noindex, follow” />
By using this directive, search engines will still crawl the page but won’t include it in their search results. Additionally, you can use the nofollow attribute if you don’t want bots to follow the links on that page.
However, it’s essential to use these tags correctly. Improper usage can unintentionally block access to important pages and links that contribute to your website’s traffic.
During technical SEO, it’s crucial to carefully manage the usage of noindex and nofollow tags to avoid slowing down the crawling of your site and affecting the crawl budget allocated by search engine bots.
Technical optimisation on MOXX
During Technical SEO, we utilise a variety of tools, plugins, and modules to enhance various factors and metrics. Technical SEO forms the foundation of a website or online store, ensuring it performs optimally and attracts more customers. Through our experience and expertise, we’ve encountered numerous scenarios and gathered knowledge to handle each of them effectively. Ignoring the importance of technical SEO can hinder your website’s performance, so it’s crucial to prioritise it.
Technical SEO in plain terms
Our team has over 10 years of experience and a wealth of know-how, focusing on technical SEO, with the primary goal of ensuring website speed. However, this is not the only aspect of optimisation that we cover. Here are some of the services we provide:
- Making code corrections.
- Building internal links.
- Implementing redirects.
- Handling canonicalization.
- Managing robots.txt.
- Creating and managing a sitemap.
- Fixing 4xx and 5xx errors.
After search engines have discovered, crawled, interpreted, and indexed the pages on your website, we take care to ensure smooth organic ranking.
The path to success with technical SEO.
Do you already have a website or are you considering having one? In both cases, you will need technical SEO from a specialist. Our team will assist you promptly!




