In the following lines, we will explore the types of e-commerce, the numerous advantages of e-commerce, key trends in e-commerce, and other important topics related to online shopping from the perspective of e-store owners and the creation of online stores.
Benefits of e-commerce
E-commerce is not a trend or a temporary mood, and it is not likely to disappear soon. Why? The sale of goods and services online is beneficial for both sellers and buyers.
Benefits for the buyer:
- Convenience in shopping;
- Faster and easier transactions;
- Informed purchase decisions;
- Easier comparison of prices and products;
- Improved delivery process;
- Targeted communication.
Benefits for the seller:
- Lower operating costs due to the elimination of physical selling locations;
- The possibility of selling products 24/7 (compared to traditional store hours);
- The opportunity to reach customers beyond geographical locations;
- Greater control over the sales process and tracking, especially if there is a portal serving sales points;
- Greater visibility to potential customers through SEO; –
- Greater control over personnel costs and resource management.
All these benefits for sellers and buyers are just the tip of the iceberg.
Trends and statistics in e-commerce
The most significant trend in e-commerce at the moment is its uncontrollable growth, taking various new forms in the conduct of buying and selling.
Over the last 10 years, e-commerce in the USA has experienced tremendous growth. Data from the US Department of Commerce shows that in 2017, e-commerce sales in the USA grew faster than they had since 2011, constituting 49% of the growth in total retail sales. This growth trend shows no sign of slowing down. Statista predicts that by 2024, online sales of physical goods in the USA will reach nearly $476.5 billion.
Global e-commerce is also expanding rapidly. Emarketer trend data indicates that retail e-commerce sales exceeded $4.058 trillion as early as 2020. As more buyers seek products from international markets, the rise in e-commerce sales is evident worldwide.
ComScore data reveals specific industries experiencing rapid e-commerce growth. Jewellery and watches lead the growth chart (as of 2016) with a 39% increase, followed by furniture, appliances, and equipment (26%), and video games/accessories (24%).
This statistical data predates the COVID-19 crisis, which further altered consumer habits and, consequently, the market. Sellers began seeking and developing even more innovative forms of online sales, contributing to the steep rise in e-commerce statistics.
Types of e-commerce
There are three classifications of e-commerce based on who is selling to whom. This classification influences the layout of online stores and sales websites tailored specifically for online merchants.
- Business to Business (B2B):
Goods and services are sold from one company to another. For example, a corporation providing products to other companies aiming for better development.
- Business to Consumer (B2C):
Businesses sell to consumers, one of the most common forms of e-commerce. Examples include online clothing stores or the online segment of a popular business consolidating sales of various products from different manufacturers.
- Consumer to Consumer (C2C):
Consumers sell directly to other consumers through online marketplaces. There are numerous websites facilitating this type of e-commerce.
How to start your e-commerce business
The following steps provide a direct guide on what you need to do sequentially to start an online business:
- Evaluate the audience and product demand.
- Research the competition.
- Explore business models and sales strategies.
- Name your business and register it.
- Create your branding and design a logo.
- Develop your product base.
- Determine production costs and processes.
- Research and set up shipping and fulfilment processes.
- Purchase a URL and create your website.
- Develop a marketing plan to attract and convert customers.
- Establish social media profiles and start building followers.
- Launch your online store.
While executing the above steps and creating your online store, keep in mind the following best practices for marketing and e-commerce websites. It’s advisable for the success of your business to involve professionals from a digital marketing firm in the development process.
E-commerce software (CMS)
When choosing the best e-commerce platform and software – such as an e-commerce website builder – that suits your needs, several factors should be taken into account.
Themes and customisation options: Ready-made themes should be customisation, allowing you to create an online store and add your logo.
Customising the domain name: You should obtain a personalised domain name and URL (so that you don’t have to include the platform’s name in your website’s URL).
24/7 expert support: If an emergency arises, you should be assured of quick and reliable technical support at any time. Initially, the company creating the store may handle support, but you will be trained to handle such situations. Ultimately, if the situation is out of control, professionals will intervene.
Flexible payment options: Customers today want to pay in various ways – from credit cards to digital wallets, etc. Seek e-commerce software that is flexible enough to support many secure payment options.
Multilingual capabilities: Your customers may come from around the world, so you should be able to speak their language. It’s a good idea to work with a tool that supports many languages, making your online store optimised for multilingual support.
Optimising your online store
Optimising e-commerce involves a wide range of strategies and tactics to convert more website visitors into customers, but two of the most crucial ones are:
Crafting compelling product descriptions: Use persuasive copywriting triggers to make your product descriptions sell. This involves employing psychological tactics such as fear of missing out on product benefits, reciprocity, exclusivity, and more, all of which encourage website visitors to make purchases (at the moment).
Using beautiful product images: When it comes to marketing, visualisation is crucial—especially for online shoppers who can’t see or touch products before making a purchase. In addition to static product images, add context by including images of models using the product and videos that provide customers with a 360-degree view.
Creating a stellar customer experience: Customer experience displaces price and product as the main factor in differentiating a brand in sales. It’s essential to focus on creating an impressive customer experience at all different touch points of your brand.
Additional ideas to start with:
Adding a frequently asked questions (FAQ) page: FAQs on your e-commerce website help potential customers quickly and easily find the information they need to complete a purchase.
Tactics for fast loading: Research indicates that more than half of website visitors expect a page to load in less than two seconds. If it takes more than three seconds, they leave the page (and are unlikely to return). Implement tactics to create a responsive website that loads quickly.
Utilising user-generated content: Incorporating user-generated content (think customer reviews, social media images, and recommendations) into your e-commerce site adds elements of social proof, which can enhance the overall customer buying experience.
Increase sales on your website
We’ve seen earlier in the text about the rapid growth of e-commerce on a global scale. Countless people are searching for various products and services online. If you’re building an e-commerce business, you need to develop a strategy to increase sales and grab a share of this market.
You won’t have an e-commerce business without customers. Therefore, consider this one of the most critical sections in this article. Let’s explore a few ways to work on increasing your e-commerce sales.
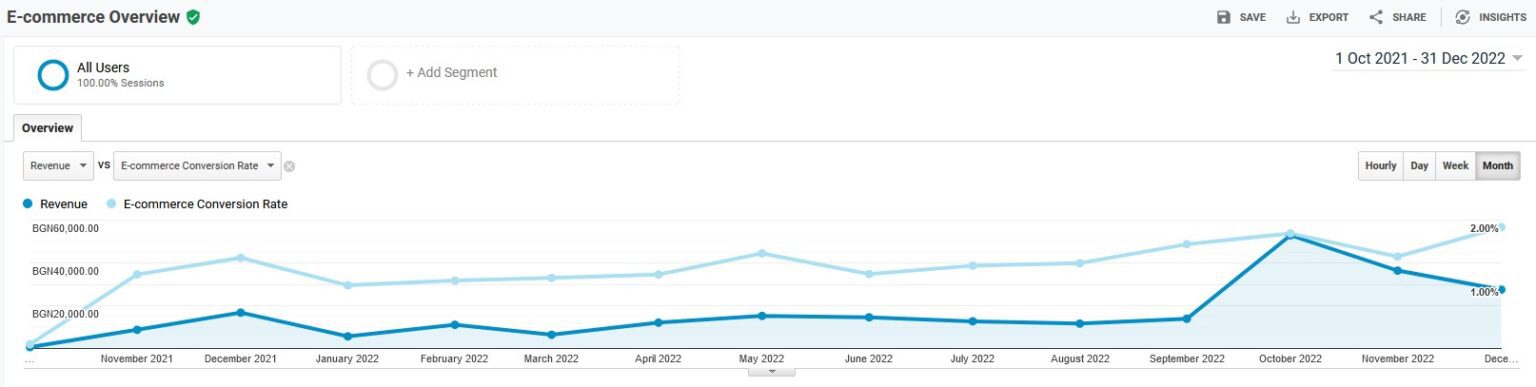
Attracting customers at the awareness stage
If you’re trying to reach potential buyers at the decision-making stage, you’re already late. Conversely, if you provide relevant content at the awareness stage and don’t take subsequent actions, you risk them forgetting about you as they move along the buyer’s journey.
It’s also essential to remember that people go through buying cycles and can move back and forth between stages before committing to a product or service. Once you attract a potential customer with your content, maintain their engagement and send them content that matches their current stage. Your goal should be to make it onto their shortlist of potential purchases.
Paid targeting to outpace competitors:
There’s a reason why paid content platforms on e-commerce sites are so profitable – they work. Search engines return billions of results daily, and many of these results are for products and services, just like yours. The problem is competition. When done correctly, paid advertising can position your e-commerce store in front of the right audience and outpace the competition.
Sharing information before customers leave
Not everyone visiting your e-commerce store is ready to make a purchase – at least you can engage them. Consider the reasons someone might visit and bounce from your page (maybe they’re considering options, find your product too expensive, or want to make a more informed decision).
Whatever the reason, your task is to provide them with something that will keep you at the forefront of their minds as they continue their search. Ideally, you’ll gather some lead information, but at a minimum, offer something useful that can assist them in their search.
Investing in customer retention
Abandoning shopping carts is inevitable, but not irreversible. Sometimes, customers just need a little nudge to return to their carts, whether through remarketing or a simple email reminder. Before reaching out to them, however, don’t forget to pay attention to some of the most common reasons potential customers initially abandon their shopping carts.
Integrating social media
Do not underestimate the power of social media when it comes to online sales. Instagram reports that 60% of people discover products on social media, making it logical to integrate shopping-related content. Meet your potential customers where they are, eliminating friction in the purchasing process by seamlessly guiding them towards making a purchase.
Best practices for e-commerce digital marketing
What do you need to know about marketing for e-commerce businesses? Here are some best practices that can help you kick start your efforts.
Test social media ads:
With its 1.18 billion daily active users, Facebook has an enormous audience that can be tapped into. Consider directing your audience to social media posts and videos, experimenting to see what works best to boost sales and revenue.
Collect email addresses and stay connected
Recent data shows that three-quarters of companies agree that email marketing offers “excellent” to “good” return on investment. By collecting email addresses on-site and asking customers to subscribe for future communications, you can give visitors a reason to return to your e-commerce site through offers, sales, VIP discounts, and more.
Use personalisation to tailor offers/messages
Personalisation is more critical than ever for online shoppers. Studies show that 74% of online consumers are disappointed when websites display offers, ads, and promotions that have nothing to do with their interests.
Make sure to use personalised product recommendations, personalise your email marketing efforts, and strive to make each customer feel like you’re speaking directly to them.
Gather feedback through surveys
The best way to keep your finger on the pulse of what your audience wants is to ask them. Use online surveys to gather feedback on everything from your product to your marketing efforts and customer interactions.
Choose e-commerce software that meets your needs and goals
You might be wondering how to ensure you’ve chosen the right e-commerce software for your specific business. Here are a few tips.
To run a successful e-commerce business, you must meet the most efficient technical requirements for e-commerce websites, ensuring that the entire business runs smoothly and offers a seamless user experience. These requirements include hosting platforms, security protocols, business operations like shipping, and operating systems.


